
How do you know when your equipment needs maintenance? Do you trust your gut or follow manufacturer recommendations? Or maybe wait until it breaks...?
Here, we discuss some of the maintenance triggers which will help you patch up, rather than bring the whole equipment down. Before we jump in, let's look at different types of maintenance.
Types of Equipment Maintenance
There are four types of maintenance strategies implemented for the care of equipment. Each strategy is differentiated from the others based on the tasks involved.
-
Reactive Maintenance;
Reactive Maintenance is conducted after machinery breaking down in order to restore it to working order.
-
Preventive Maintenance;
Preventive maintenance aims to ensure the equipment maintains a level of functionality by regularly conducted inspections. Preventive maintenance involves tasks such as visual inspections, lubrication, cleaning, etc.
-
Predictive Maintenance;
This type of maintenance requires constant knowledge of the status of equipment and its operational capacity. The identified values of variables enable you to determine the performance levels of the machinery and monitor for future failure in order to plan maintenance before the failure occurs.
Preventive Maintenance
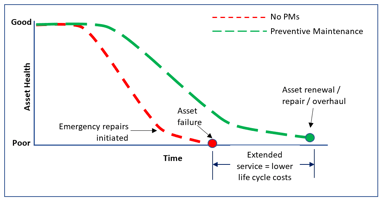
Preventive maintenance is essentially performed to reduce the chances of equipment failure, making sure that every piece of equipment receives consistent maintenance to prevent costly and unexpected breakdowns.
While some companies opt for reactive maintenance; where a piece of equipment is fixed only after failure, preventive maintenance is often less costly. This is because it saves your company from the costs incurred from unplanned equipment failures such as;
- Lost production
- Expedited shipments
- Overtime
- Shorter equipment life expectancy
- Increased downtime
- Safety issues
For preventive maintenance, the maintenance is set based on a schedule often recommended by the manufacturer of the equipment.
Alternatively, preventive maintenance can be set based on maintenance triggers, which are indicators that alert employees on the need for maintenance. A CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) will allow you to monitor the status of the equipment and alert you when maintenance is required based on the triggers set.
The CMMS, sometimes referred to as Enterprise Asset Management (EAM), is designed to make maintenance management easier. A CMMS enables organizations to track work orders, and generate timely and accurate reports that help them determine which machinery needs preventive maintenance.
Additionally, CMMS software also makes it possible for technicians to correctly prioritize the tasks involved in their work orders, identifying and attending to the most critical maintenance jobs as soon as possible.
Different types of CMMS solutions offer various types of systems. The best CMMS or EAM software is one that makes it possible for the user to accomplish maintenance tasks more effectively and timely, leading to a reduction of costs incurred.
Other advantages of implementing a CMMS include;
- Enhanced management of work orders
- Increased equipment life span
- Improved management of inventory
- Reduced downtime and increased productivity
- Enables you to make data-based maintenance decisions
- Enables you to meet safety and compliance standards
- Increased asset reliability
- Gives you better insight into operations
- Makes it possible for you to save on labor time
Implementing CMMS software goes a long way in ensuring your preventive maintenance program is as effective as possible. However, for even more effective maintenance operations, consider implementing the different types of maintenance strategies during your equipment's life cycle.
To determine the type of maintenance strategy to put in place, identify whether;
- The asset is critical to business operations
- It's safety contributions are critical
- The business will be disrupted if the asset breaks down
- The repair or replacement of the asset would be a costly endeavor
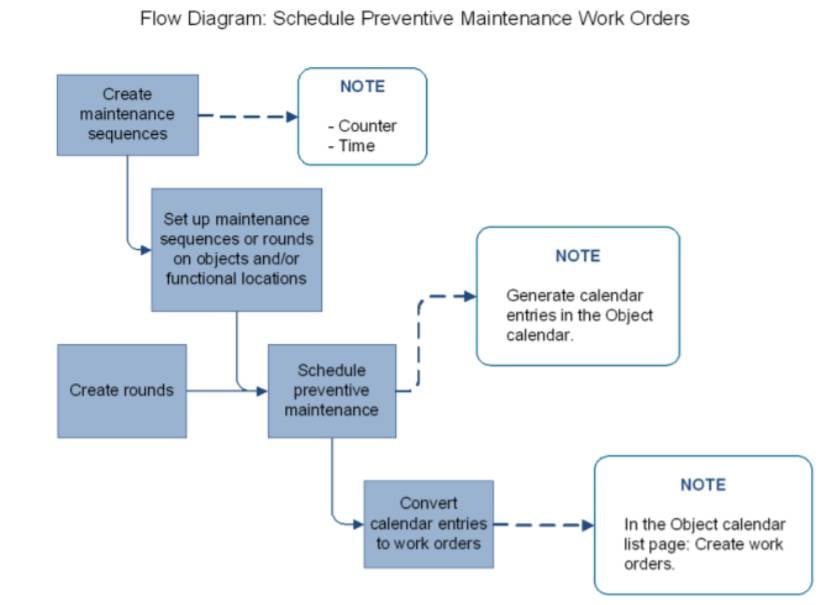
Maintenance Sequences
Preventive maintenance is a discipline involving planned maintenance jobs, for example, regular service, calibration, and inspections. You can create maintenance sequences and set them up on objects or functional locations. Also, you can read counter registrations (production hours or quantity produced) on your equipment and subsequently create counter registration records on the objects. The counter registrations are used in preventive and reactive maintenance scheduling.
Maintenance sequences can be set up on objects or functional locations. Instead of setting up maintenance sequences on objects, you can create rounds that include multiple objects on which you need to perform related types of maintenance jobs in the same work routine. Maintenance sequences are used for preventive and reactive maintenance on individual objects. Rounds are used for preventive maintenance on a group or a set of objects.
A maintenance sequence defines when a pre-planned preventive maintenance job is to be carried out on an object. Maintenance sequences can be related to objects, object types, functional locations, or functional location types. There are two types of maintenance sequences:
Time trigger
Here, the maintenance of a piece of equipment is scheduled based on a determined schedule. When the time arrives, a technician is notified, and the work order is completed.
Time triggers are a part of preventive, predictive, and condition-based maintenance. Scheduling regular maintenance tasks ensure that the equipment is functioning as required and also allows you to identify issues early on before they lead to costly equipment break downs.
In Dynaway EAM a maintenance sequence defines when a pre-planned preventive maintenance job
is to be carried out on an object. Maintenance sequences can be related to objects, object types, functional locations, or functional location types. Examples of preventive maintenance sequences of type "Time" are "Repeated from start date", "Repeated from last work order", and "Linked from last work order" (repeated after every completed work order).
Counter trigger
Counter triggers happen when maintenance on equipment is done after functioning at a certain output. When an asset meets a predetermined usage point, it triggers a maintenance work order. This kind of trigger is another indication of predictive, condition-based, or preventive maintenance. Usage triggers are best suited for equipment that is either irregularly or heavily used, vital for production and have detectable usage-based failure rates. A good example of Counter Trigger could be that a belt needs to be inspected after 100 hours of production.
Examples of reactive maintenance sequences in Dynaway EAM of type "Counter" are "Once reached above" (validating against upper limit) and "Once reached below" (validating against a lower limit).
Breakdown Trigger
By using IoT sensors and counter sequences you can set up specific conditions which would determine if the equipment is down. The moment a piece of equipment breaks down, work order is pushed to workers and maintenance efforts are put in place to rectify the issue and get the equipment operational. The types of maintenance that make use of breakdown triggers include reactive, run-to-failure, and corrective maintenance.
While maintenance is not put in place when using this kind of trigger, there is still a plan to handle breakdown if it occurs.
Breakdown triggers are generally meant for assets that are not critical to the business' operations or assets that can be quickly fixed or replaced with minimal costs.
Condition trigger
Condition triggers review how an asset is operating; when an asset is not functioning in the intended manner, it could be a sign of an impending failure. When conditions such as overheating are discovered, work orders are triggered to address the cause of the condition and rectify it.
If an asset is not functioning right, alerting a technician makes it possible for the asset to be checked, rectified, and returned to standard operation. Tracking equipment condition can range from visual inspections to technical means such as vibration analysis.
Make sure you cover all steps!
Continue to read: All you need to know about Preventive Maintenance




-1.png?width=388&height=200&name=Webinar%20MS%20AM%20Mobility%20(2)-1.png)
