.png?width=693&height=456&name=Copy%20of%20Blog%20Feature%20Image%20(4).png)
As the technologies advance, so do the challenges companies face.
Challenges have changed from managing complex machinery to optimizing processes for peak efficiency. In the busy world of industrial operations, where precision, productivity, and cost-efficiency are essential, organizations are constantly looking for innovative solutions to remain successful and stay ahead of the competition.
At the core of this quest for excellence, one paradigm-shifting concept – Predictive Maintenance - has emerged as a potential game-changer in maintenance management.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Predictive Maintenance (PdM) is a game-changing concept in maintenance management. It involves data analysis and machine learning to detect or predict equipment failures, maximize efficiency, and extend the useful lifetime of asset components.
- AI implementation raises concerns about transparency, reliability, costs, and job displacement, which must be effectively tackled.
- When aiming for predictive maintenance, it's advisable to begin with condition-based monitoring, taking small steps while utilizing available data sources.
- Careful selection of the AI method is crucial, considering data availability and expert knowledge. Bayesian networks are a transparent and explainable AI method suitable for managing uncertainty.
What exactly is the concept of Predictive Maintenance?
To answer this question, let us consider the difference between corrective, preventive, and predictive maintenance.
| Corrective Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
| A reactive approach to addressing equipment failures after they have occurred. It involves the repair or replacement of faulty components, often leading to unscheduled downtime and higher repair costs. | A proactive approach where scheduled maintenance tasks or equipment replacements are performed at predetermined intervals. Its main objective is to prevent equipment failures, thereby minimizing unplanned downtime and reducing the likelihood of high-cost repairs. |
A more advanced approach to maintenance that applies data analysis of, e.g., sensor readings to detect or predict when the likelihood of equipment failure is increasing. |
Corrective maintenance is generally less cost-efficient than the other two approaches due to the management of unexpected breakdowns.
Predictive maintenance is the most advanced approach uses data and machine learning algorithms to make models for detecting or predicting failure, thereby extending the useful lifetime of components and maximizing efficiency. The objective is to use data analysis to take into consideration that the working environments and operation conditions influence the degradation of equipment to support maintenance planning before the failure occurs.
Predictive maintenance can help eliminate or reduce the days of costly downtime, unexpected breakdowns, and reactive chaos. With predictive maintenance, organizations are not only anticipating maintenance needs; they are changing their entire approach to maintenance.
Revolution of Artificial Intelligence
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has received increasing attention as a methodology to potentially transform how organizations operate.
Artificial Intelligence is not a threat but an opportunity to solve problems more efficiently. It is not a new concept - John McCarthy et al. introduced Artificial Intelligence as a research area as part of the Dartmouth workshop in the 1950ties. At the same time, Alan Turing discussed "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" in 1950.
Artificial Intelligence - in one form or another - is already used in our daily lives in a wide range of areas, such as medical diagnosis (e.g., image analysis), credit default prediction, identification of credit card fraud, and online chatbots, to name a few.
There exist several different Artificial Intelligence methods ranging from rule-based systems relying on expert knowledge to deep neural networks and the more recent large language models (used in, for instance, ChatGPT), where the latter two rely on access to vast amounts of data.
The need for huge amounts of data can be a challenge in many domains, especially in maintenance, where, on the other hand, a lot of expert knowledge may be available. For that reason, it is crucial to carefully choose the right Artificial Intelligence method to implement predictive maintenance.
Application of Artificial Intelligence
The application of Artificial Intelligence in industry is often met with some degree of skepticism caused by concerns related to transparency, reliability, and unintended consequences. Even though the use of Artificial Intelligence offers many potential benefits, there are a few concerns about it when it comes to maintenance activities.
Some of the main problems relate to data availability and quality, transparency and explainability of AI models and results, initial costs and return on investment, and employees' fear of technology eliminating jobs. It is the responsibility of management to address these concerns, and they can be efficiently handled by using the right approach, the proper methodology, and employee involvement.
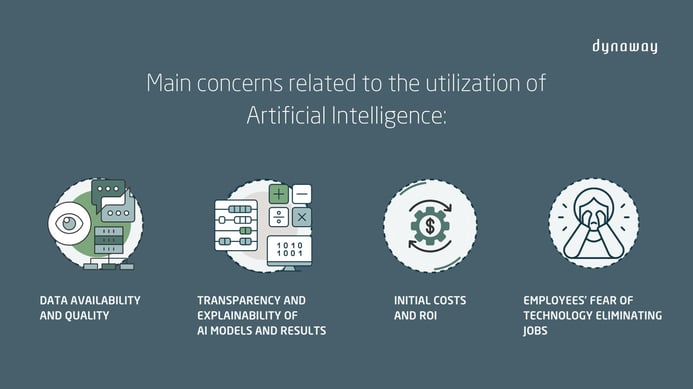
To guarantee a successful integration of AI, it's imperative to confront these concerns and implement best practices. Below, we outline some key strategies for effectively leveraging the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence in the maintenance domain.
Best Practices for AI implementation
1. Build trust and employee empowerment in AI implementation
It is essential to engage maintenance staff and other employees in the development process to ensure an open process that engages all relevant members of the organization. Management must support the efforts to develop and implement the use of Artificial Intelligence to provide the necessary level of commitment from the organization.
Management support, employee involvement, and transparent AI methods are vital to reduce skepticism and resistance when implementing new technologies, especially Artificial Intelligence. Building trust in the organization is crucial during the implementation process.
2. Consider the human-in-the-loop approach
The aim is not to replace maintenance staff but to supply decision support to maintenance staff to improve the efficiency of the maintenance process. Artificial Intelligence systems should not replace staff members but empower them with a tool to improve efficiency.
3. Start small and think big
With predictive maintenance as the long-term goal, it may - depending on the maintenance management maturity of the organization - be most efficient to start the journey with condition-based monitoring, taking small steps at a time. Start small, think big. The process of applying Artificial Intelligence in maintenance should begin by clearly defining the equipment to consider and by identifying the available and accessible data and information sources (e.g., knowledge and experience from operators and maintenance staff).
Do not start the process by collecting new data for a long time. Start with whatever is already available or easy to collect.
4. Choose the right AI method for your needs
There are different Artificial Intelligence methods that can be applied, and they have different strengths and weaknesses. It is important to carefully select the method to apply to meet the requirements of the problem to solve and where the necessary information (e.g., historical data and expert knowledge) to formulate the Artificial Intelligence model is available or can readily be obtained.
Let's dive into one of these methods.
Bayesian Networks
The framework of Bayesian networks is an Artificial Intelligence method capable of combining historical data and domain expert knowledge into a single knowledge representation that is transparent and explainable.
Bayesian network is a representation well suited for managing uncertainty as it is based on (conditional) probabilities and can represent uncertain cause-effect relations. The probabilistic-based approach means that noisy data and missing values in the data are not a problem, while the hierarchical structure and support for cause-effect relations mean that the model can reflect the structure of the equipment being modeled. This increases trust in the model and its results. Due to the intuitive graphical nature of a Bayesian network, it encourages stakeholder involvement in the model development process where historical data and expert knowledge are fused into a single knowledge-integrating model.
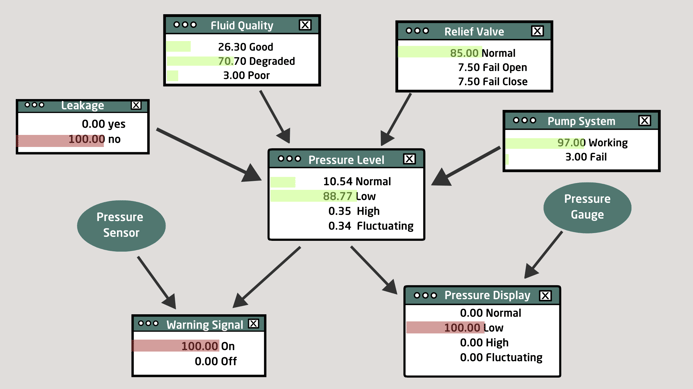
Based on the data (red bars), the conclusion is that the Pressure Level is low due to Fluid Quality being degraded.
PredictIT is a new solution that is based on Bayesian networks. It is tailored to address challenges in areas like condition-based monitoring, predictive maintenance, and root cause analysis. In an upcoming article, we will describe the use of PredictIT and Bayesian networks in a real predictive maintenance application.
AI could be the future of predictive maintenance, and we are here to help make sure you are ahead of the curve.
Stay tuned!
McCarthy, J., Minsky, M.L., Rochester, N. and Shannon, C.E. (1955) A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence (Hanover, NH., Dartmouth College)
Turing, A.M. (1950) ‘Computing machinery and intelligence’ Mind, 59 (236), 433–60


.png?width=388&height=200&name=Copy%20of%20Blog%20Feature%20Image%20(6).png)
.png?width=388&height=200&name=Copy%20of%20Blog%20Feature%20Image%20(4).png)


