
The importance of employee safety, in all contexts within a manufacturing or industrial environment, cannot be overstated. It is just as important to safeguard workers for the sake of good ethics as it is for the bottom line of an organization.

Maintenance and repair operations are among the settings in which serious or deadly accidents can occur if proper precautions aren't strictly observed, including those falling under the umbrella of lockout tagout. Understanding lockout tagout procedures is critical to ensure worker safety in any facility, and we will explore them in Part 1 of this blog series.
What is lockout tagout? The basics
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) defines lockout tagout as "practices and procedures necessary to disable machinery or equipment, thereby preventing the release of hazardous energy while employees perform servicing and maintenance activities."
More simply, it's the process by which you make sure any equipment scheduled for upkeep operation is powered down, rendered inoperable and, as necessary, isolated from general workspaces and nearby personnel. The terms "lockout" and "tagout," respectively, refer to locks (literal or otherwise) used to prevent equipment use and notices warning workers of applicable hazards. (Sometimes, only tags are used, but these practices in general are almost invariably called "lockout tagout" or "LOTO" no matter what.)
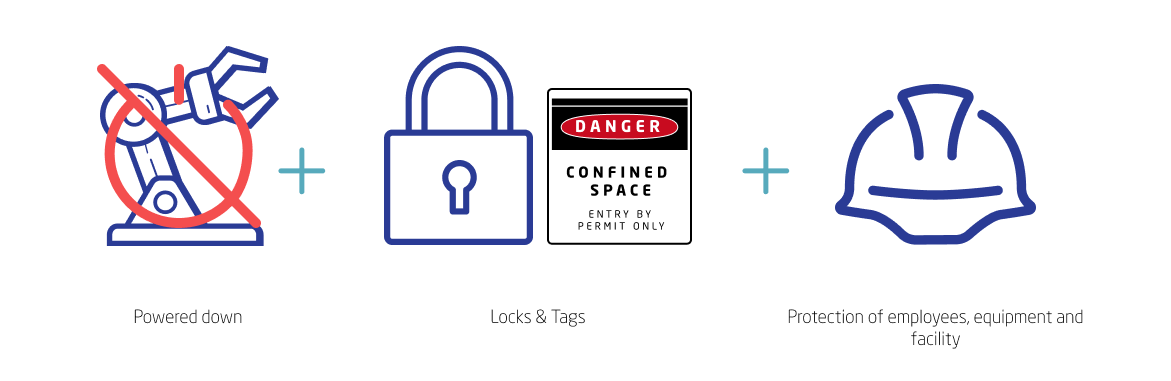
Lockout tagout procedures are observed for any machines or devices that could potentially injure workers during maintenance, either through mechanical operation or the sudden release of stored energy. (The latter category encompasses hazardous energy sources ranging from steam and fire to electricity, explosives and volatile chemicals.) Any facility that uses equipment, vehicles or devices capable of causing such harm owes it to its workers to shield them from such hazards in all contexts: Manufacturing, oil and gas, chemical processing, construction and public utilities are just a few examples of industries where lockout and tagout are critical.
The various lockout tagout steps are generally codified as a single policy that all workers must follow, in the interest of promoting and maintaining coherent practices throughout the organization. Not only are locks and tags used to seal off and identify equipment in need of maintenance, but each application and removal of a lock or tag must also be tracked, with notes included that identify individuals responsible for all of these occurrences. Lastly, an organization's lockout tagout procedure will usually specify that only certain employees can lock out, unlock, tag out or untag equipment.
Why is lockout tagout important?
The first and biggest reason why lockout tagout matters is the protection of your company's people. They are, without a doubt, your most valuable asset: While most hardware can, one way or another, be replaced, there's no guarantee of being able to replace any of your skilled and experienced workers. Employees can be seriously hurt while performing even routine maintenance operations if machines or equipment have not been properly detached from every energy source, locked out and, in applicable situations, had any stored energy released in a safe manner.
Machines can also cause significant damage to themselves or the facility as a whole if they malfunction or unexpectedly release hazardous energy. As stated, this isn't quite as serious as an employee injury or death — which has both a moral and financial impact — but it would be notably detrimental to the bottom line.
Moreover, any failure to adhere to an established LOTO program that engendered a lapse in compliance with an OSHA standard, ATEX guidelines or any other relevant regulation can trigger costly fines, lawsuits filed against you for negligence and possibly even criminal charges. It will also virtually guarantee that regulators will view your organization with greater scrutiny going forward (at least until you prove compliant over a sustained period).
Last but not least, accidents of any kind can diminish the public reputation of your organization and severely damage worker morale: After all, few if any individuals with the proper skills to hold positions in your business will be enthused to work for a company that doesn't have a strong safety record and a firm energy control procedure in place or has received repeated violations. For all of these reasons, lockout tagout is critical to ensure accurate and comprehensive documentation of your company's safety activities.
Key lockout tagout safety requirements
The specific lockout procedure in your organization will depend on the type of equipment you have at your facility and the hazards that it may pose. That said, there are certain baseline standards that should apply across the board to virtually any manufacturing or industrial company's lockout tagout process:
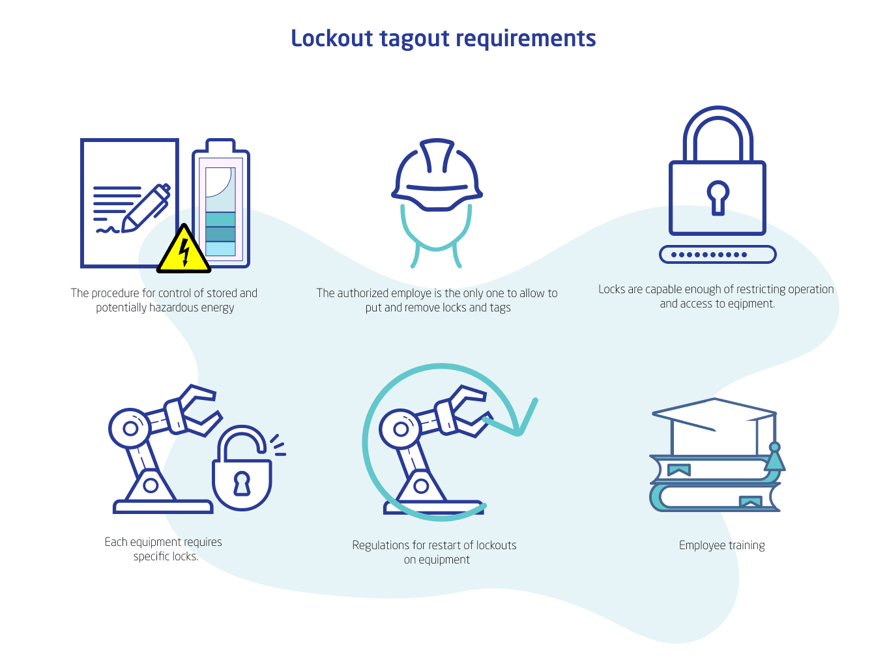
- Establish, implement and adhere to a specific procedure for controlling stored energy, as hazardous energy release is arguably the biggest danger that maintenance team members face while inspecting or repairing a device. This set of energy control standards should be reviewed at least once a year to ensure it remains relevant and sufficient.
- Restrict the use of each lockout or tagout device to an authorized employee — ideally, the worker who applies a lock, tag or both to a machine should be the only person who removes it.
- Make sure any locks used are capable of restricting operation of and/or access to the equipment with which they are associated, regardless of situational or environmental hazards. (For example, a lockout device used in any oil and gas industry applications must be highly corrosion-resistant and maintain its integrity in extreme-temperature conditions.)
- Along similar lines, specific equipment requires specifically authorized locks.
- If only using tagout materials, make sure you are confident that they will be enough to deter any individuals from operating or approaching a tagged machine or system.
- Companies subject to ATEX regulations will need restart lockouts for any machines with emergency stop controls.
- Set up employee training to teach all of these requirements to workers (as well as any others that apply to lockout, tagout or energy isolation).
We will explore the more detailed ins and outs of LOTO procedure in the next installment of this blog series. In the meantime, learn more about how Dynaway's Safe Work module can help improve safety procedures for any organization.


%20%5BConverted%5D-1.png?width=388&height=200&name=Illustration%20(45)%20%5BConverted%5D-1.png)


%20%5BConverted%5D-1.png?width=388&height=200&name=Illustration%20(46)%20%5BConverted%5D-1.png)
